Dear Reader,
We often hear about the circulatory system, the intricate network of arteries and veins that tirelessly delivers oxygen and nutrients throughout our bodies. However, there's another equally vital, yet often overlooked, network working silently behind the scenes: the lymphatic system. Far from being a simple drainage system, the lymphatic system plays a crucial role in our immunity, fluid balance, and overall health. Understanding its functions and how to support it can empower us to take better care of our well-being.
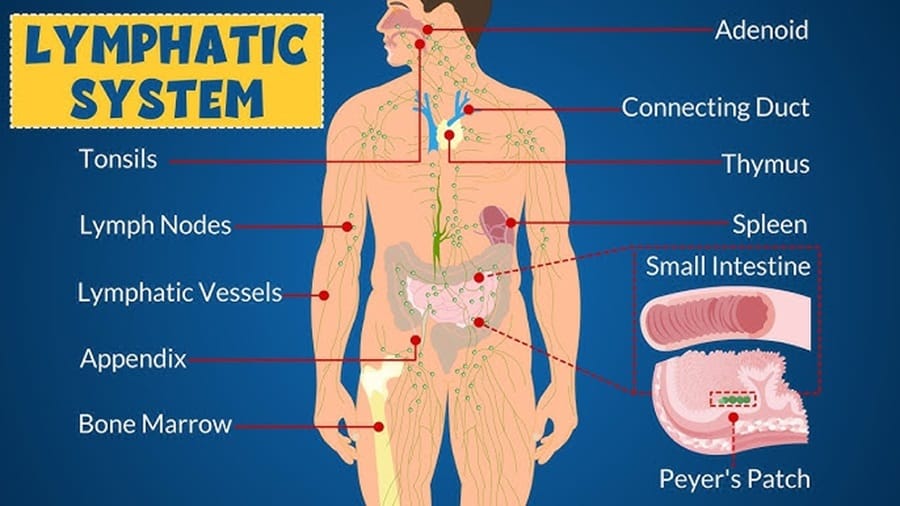
Imagine a complex network of tiny vessels, similar in appearance to veins, weaving their way through almost every tissue in your body. This is the lymphatic system. Unlike the circulatory system, which has the heart as its central pump, the lymphatic system relies on muscle contractions, movement, and even breathing to circulate its fluid, called lymph.
So, what exactly does this unsung hero of our physiology do? The lymphatic system has three primary functions:
1. Fluid Balance: Preventing the Swell
Every day, our capillaries – the smallest blood vessels – leak a small amount of fluid into the surrounding tissues. This fluid, now called interstitial fluid, delivers vital substances to our cells and collects waste products. Without a proper drainage system, this fluid would accumulate, leading to swelling or edema. This is where the lymphatic system steps in.
Tiny lymphatic capillaries, with their unique one-way valves, collect this excess interstitial fluid. Once inside the lymphatic vessels, the fluid is called lymph. The lymphatic vessels then transport this lymph towards larger collecting vessels, eventually returning it to the bloodstream near the heart. This constant drainage prevents fluid buildup and maintains the delicate balance of fluids in our tissues. Think of it as the body's natural flood control system.
2. Fat Absorption: Nourishing Our Cells
The lymphatic system also plays a crucial role in the absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins from the small intestine. Specialized lymphatic vessels called lacteals, located in the lining of the small intestine, absorb dietary fats that are too large to be directly absorbed into the bloodstream. This fat-rich lymph, called chyle, travels through the lymphatic vessels and eventually enters the bloodstream, providing essential nutrients for our cells and energy production. This unique function highlights the lymphatic system's integral role in our digestive health.
3. Immune Defense: Our Body's Surveillance Network
Perhaps the most critical role of the lymphatic system is its involvement in our immune response. As lymph circulates throughout the body, it passes through numerous bean-shaped organs called lymph nodes. These lymph nodes are strategically located throughout the body, including the neck, armpits, groin, and abdomen, acting as filtration and surveillance centers.
Lymph nodes contain specialized immune cells, such as lymphocytes (including B cells and T cells) and macrophages. As lymph flows through the nodes, these immune cells identify and attack foreign invaders like bacteria, viruses, and cancerous cells. Macrophages engulf and destroy pathogens and cellular debris, while lymphocytes mount specific immune responses, producing antibodies and directly attacking infected cells.
When the body is fighting an infection, the lymph nodes in the affected area often become swollen and tender. This is a sign that the immune cells within the nodes are actively working to combat the threat. The lymphatic system, therefore, is a critical component of our body's defense mechanism, protecting us from a constant barrage of potential threats.
Supporting Your Lymphatic System: Simple Steps for Better Health
Given the vital roles of the lymphatic system, it's essential to support its healthy function. Fortunately, several simple lifestyle adjustments can make a significant difference:
Stay Hydrated: Lymph is primarily composed of water, so adequate hydration is crucial for its proper flow and function. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Engage in Regular Movement: Unlike the circulatory system with its dedicated pump, the lymphatic system relies on muscle contractions and movement to circulate lymph. Regular exercise, even gentle activities like walking, swimming, or yoga, can significantly improve lymphatic drainage.
Practice Deep Breathing: Deep, diaphragmatic breathing can also help stimulate lymphatic flow. The expansion and contraction of the diaphragm create a gentle pumping action that aids in the movement of lymph.
Consider Gentle Massage: Specific massage techniques, known as lymphatic drainage massage, can help to manually stimulate lymph flow and reduce swelling. You can learn simple self-massage techniques or consult a trained therapist.
Maintain a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients that support overall health, including the lymphatic system. Limiting processed foods, excessive sugar, and unhealthy fats can also benefit lymphatic function.
Avoid Tight Clothing: Restrictive clothing can impede lymphatic flow, especially around areas like the neck, armpits, and groin where lymph nodes are concentrated. Opt for looser, more comfortable clothing.
When to Seek Professional Advice
While supporting your lymphatic system through lifestyle choices is generally beneficial, certain signs and symptoms may indicate a lymphatic issue requiring medical attention. These include persistent swelling (especially in one limb), unexplained fatigue, recurrent infections, or noticeable lumps or bumps in the lymph node areas. If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to consult your doctor for proper diagnosis and management.
Conclusion
The lymphatic system, though often operating in the background, is an indispensable network that plays fundamental roles in maintaining our fluid balance, absorbing fats, and defending our bodies against infection. By understanding its functions and adopting simple lifestyle strategies to support it, we can contribute significantly to our overall health and well-being. Let's give this silent guardian the attention it deserves.
Disclaimer
Please remember that the information provided in this newsletter article is intended for general educational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. It is not a substitute for professional medical diagnosis, treatment, or advice from a qualified healthcare provider. |
Always consult with your physician or another qualified health provider regarding any medical condition or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read in this newsletter. |
Individual results may vary, and the effectiveness of any health approach depends on various personal factors. We encourage you to discuss any health concerns or questions you may have with your doctor or healthcare team.Disclaimer |
Please remember that the information provided in this newsletter article is intended for general educational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. It is not a substitute for professional medical diagnosis, treatment, or advice from a qualified healthcare provider. |
Always consult with your physician or another qualified health provider regarding any medical condition or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read in this newsletter. |
Individual results may vary, and the effectiveness of any health approach depends on various personal factors. We encourage you to discuss any health concerns or questions you may have with your doctor or healthcare team.lease remember that the information provided in this newsletter article is intended for general educational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. It is not a substitute for professional medical diagnosis, treatment, or advice from a qualified healthcare provider. |
Always consult with your physician or another qualified health provider regarding any medical condition or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment. Do not disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read in this newsletter. |
Individual results may vary, and the effectiveness of any health approach depends on various personal factors. We encourage you to discuss any health concerns or questions you may have with your doctor or healthcare team. |
